Overview of Reducers
Key Features of Reducers
Flow Transition Efficiency
Material Versatility and Compatibility
Pressure Integrity and Structural Stability
Installation Flexibility
Types of Reducers and Their Applications
Concentric Reducers
Eccentric Reducers
Typical Applications of Reducers
Pump Suction and Discharge Lines
Pipeline Size Transition
Pipe Rack Installations
Process Equipment Connections
Technical Specifications
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
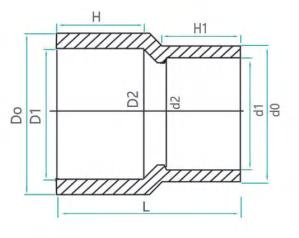
| SIZE | D1 | D2 | H | d1 | d2 | H1 | L |
| DN20X15 | 25.3 | 31.9 | 19 | 20.3 | 26.3 | 16.5 | 40 |
| DN25X15 | 32.35 | 39.5 | 22.5 | 20.3 | 26.3 | 16.5 | 47.8 |
| DN25X20 | 32.35 | 39.5 | 22.5 | 25.3 | 31.9 | 19 | 47.4 |
| DN32X20 | 40.4 | 49.8 | 26.5 | 25.3 | 31.9 | 19 | 56.6 |
| DN32X25 | 40.4 | 49.8 | 26.5 | 32.35 | 39.95 | 22.5 | 54.8 |
| DN40X15 | 50.45 | 62 | 31.5 | 20.3 | 27 | 16.5 | 66 |
| DN40X20 | 50.45 | 62 | 31.5 | 20.3 | 31.9 | 19 | 66 |
| DN40X25 | 50.45 | 60.25 | 31.5 | 40.4 | 49.8 | 26.5 | 67 |
| DN40X30 | 50.45 | 75 | 38 | 40.4 | 49.8 | 26.5 | 65.1 |
| DN40X32 | 63.5 | 75.9 | 38 | 25.3 | 31.9 | 19 | 79 |
| DN40X25 | 63.5 | 75.9 | 38 | 32.35 | 39.95 | 22.5 | 80 |
| DN40X32 | 63.5 | 75.9 | 38 | 40.4 | 49.8 | 26.5 | 80 |
| DN40X40 | 63.5 | 75.9 | 38 | 50.45 | 60.25 | 31.5 | 77.7 |
| DN40X25 | 75.5 | 88.91 | 44 | 32.35 | 39.95 | 22.5 | 93.5 |
| DN40X20 | 75.5 | 88.91 | 44 | 25.3 | 31.9 | 19 | 92.5 |
| DN40X30 | 75.5 | 88.91 | 44 | 50.45 | 60.25 | 31.5 | 93.5 |
| DN40X32 | 75.5 | 88.91 | 44 | 43.5 | 51.9 | 38 | 125.5 |
| DN40X25 | 90.55 | 105.15 | 51.5 | 32.35 | 39.95 | 22.5 | 108 |
| DN40X50 | 90.55 | 105.15 | 51.5 | 63.5 | 75.9 | 38 | 108 |
| DN40X65 | 90.55 | 105.15 | 51.5 | 75.5 | 88.91 | 44 | 107.3 |
| DN100X50 | 110.6 | 127.39 | 61.5 | 63.5 | 75.9 | 38 | 128 |
| DN100X65 | 110.6 | 127.39 | 61.5 | 75.5 | 88.91 | 44 | 128.6 |
| DN100X80 | 110.6 | 127.39 | 61.5 | 90.55 | 105.15 | 51.5 | 127.4 |
| DN125X50 | 140.6 | 161.4 | 76 | 90.55 | 105.15 | 61.5 | 138.3 |
| DN125X80 | 140.6 | 161.4 | 76 | 110.6 | 127.39 | 61.5 | 137.7 |
| DN150X100 | 160.7 | 184.5 | 86.5 | 110.6 | 127.39 | 61.5 | 180.2 |
| DN150X125 | 160.7 | 184.5 | 86.5 | 140.6 | 161.4 | 76 | 177.3 |
| DN200X115 | 200 | 228.1 | 106.2 | 110 | 127.5 | 61.5 | 217 |
| DN200X160 | 200 | 228.1 | 106.2 | 160 | 184.9 | 86.5 | 217 |
| DN200X100 | 226.2 | 253.8 | 118.5 | 110.6 | 127.39 | 61.5 | 244.5 |
| DN200X150 | 226.2 | 253.8 | 118.5 | 160.7 | 184.5 | 86.5 | 242.5 |
| DN200X200 | 226.2 | 283.8 | 131.5 | 160 | 184.9 | 86.5 | 270 |
| DN200X225 | 200 | 263.4 | 131.5 | 226 | 253.8 | 118.5 | 270 |
| DN200X225 | 281.5 | 315.5 | 149 | 226.2 | 253.8 | 118 | 304 |
| DN280X160 | 281.5 | 315.5 | 149 | 160.8 | 185 | 85 | 304 |
| DN315X225 | 316.7 | 355 | 166 | 226.2 | 253.8 | 118 | 355 |
| DN315X160 | 316.7 | 355 | 166 | 160.8 | 185 | 85 | 355 |
| DN355X135 | 356.8 | 395 | 186 | 316.7 | 355 | 162 | 385 |
| DN355X225 | 356.8 | 395 | 186 | 226.2 | 253.8 | 118 | 385 |
| DN400X135 | 400 | 442 | 208 | 316.7 | 355 | 162 | 440 |
| DN400X160 | 402 | 442 | 205 | 356.8 | 395 | 162 | 440 |