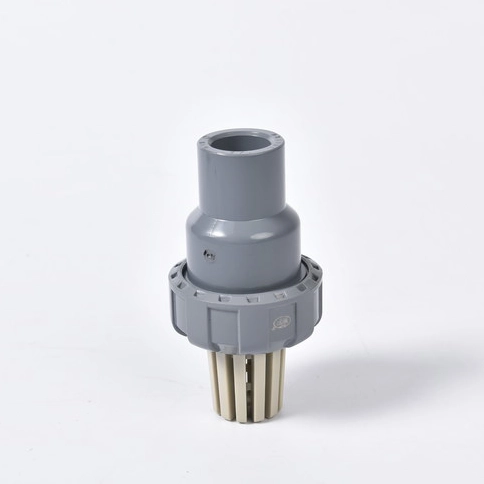
Overview of Ball Bottom Valve
Key Features of Ball Bottom Valve
Zero-Residue Design
Hygienic and Sanitary Construction
High-Performance Sealing System
Versatile Actuation Options
Robust Construction Materials
Typical Applications of Ball Bottom Valve
Pharmaceutical and Bioprocessing
Food and Beverage Industry
Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
Mining and Mineral Processing
Technical Specifications
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
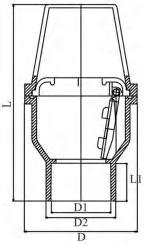
| SIZE | Number | D | D1 | D2 | L | L1 |
| 1-1/2″(DN40) | FD40 | 105.00 | 50.45 | 60.50 | 200.00 | 37.70 |
| 2″(DN50) | FD50 | 124.20 | 63.50 | 75.90 | 220.00 | 38.30 |
| 2-1/2(DN65) | FD65 | 145.00 | 75.50 | 88.91 | 260.00 | 44.80 |
| 3″(DN80) | FD80 | 163.00 | 90.55 | 105.15 | 300.00 | 56.70 |
| 4″(DN100) | FD100 | 190.00 | 110.60 | 127.39 | 370.00 | 75.10 |
| 5″(DN125) | FD125 | 247.00 | 140.60 | 164.40 | 400.00 | 95.00 |
| 6″(DN150) | FD150 | 270.00 | 160.70 | 184.50 | 485.00 | 99.90 |
| 8″(φ200) | FD200 | 344.60 | 200.90 | 225.00 | 510.00 | 124.80 |