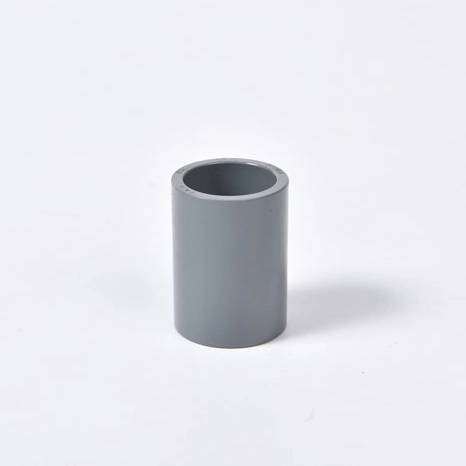
Overview of CPVC Direct Coupling
Key Features of CPVC Direct Coupling
Enhanced Thermal Stability
Superior Chemical Resistance
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Installation Efficiency and Weight Advantage
Long-Term Value and Sustainability
Typical Applications of CPVC Direct Coupling
Industrial Chemical Processing
Hot Water Distribution Systems
Fire Sprinkler Systems
Electrical Conduit and Corrosive Fume Handling
Technical Specifications
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
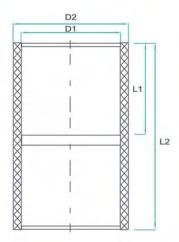
| SIZE | Number | D1 | D2 | L1 | L2 |
| DN15 | ZJ15 | 20.3 | 26.3 | 16.5 | 34.4 |
| DN20 | ZJ20 | 25.3 | 31.9 | 19 | 39 |
| DN25 | ZJ25 | 32.35 | 39.95 | 22.5 | 46.27 |
| DN32 | ZJ32 | 40.4 | 49.8 | 26.5 | 54.38 |
| DN40 | ZJ40 | 50.45 | 60.25 | 31.5 | 64.39 |
| DN50 | ZJ50 | 63.5 | 75.9 | 38 | 85.11 |
| DN65 | ZJ65 | 75.5 | 88.91 | 44 | 90.16 |
| DN80 | ZJ80 | 90.55 | 105.15 | 51.5 | 106.32 |
| DN100 | ZJ100 | 110.6 | 127.39 | 61.5 | 138.49 |
| DN125 | ZJ125 | 140.6 | 161.4 | 76 | 159.61 |
| DN150 | ZJ150 | 160.7 | 184.5 | 86.5 | 179.35 |
| dn200 | ZJ200 | 200 | 228.1 | 106.2 | 218 |
| DN200 | ZJ200 | 226.2 | 253.8 | 118.5 | 243.03 |
| dn250 | ZJ250 | 250 | 281.89 | 131.5 | 268 |
| DN250 | ZJ250 | 281.5 | 315.5 | 147 | 299 |
| DN300 | ZJ300 | 316.7 | 355 | 165 | 343 |
| DN350 | ZJ350 | 356.8 | 395 | 185 | 376 |
| DN400 | ZJ400 | 402 | 442 | 208 | 424 |
| DN250 (PN10) | ZJ250 | 280.6 | 306 | 147 | 299 |
| DN300 (PN10) | ZJ300 | 315.7 | 344 | 166 | 343 |
| DN350 (PN10) | ZJ350 | 355.8 | 385 | 183.5 | 373 |
| DN400 (PN10) | ZJ400 | 401 | 432 | 208 | 423 |