Overview of Male Thread Connector
Key Features of Male Thread Connector
-
Universal Thread Compatibility Male thread connectors are produced in standardized thread profiles (e.g., NPT, BSPT, BSPP, metric) to ensure interoperability with global piping systems . Tapered threads (e.g., NPT) create self-sealing engagements under pressure, while parallel threads (e.g., BSPP) require gaskets for leak-proof performance . This versatility simplifies system integration and component replacement across regions and industries. -
Robust Material Construction Constructed from corrosion-resistant materials such as 304/316 stainless steel, brass, and alloy steels, these connectors withstand aggressive media (acids, alkalis, solvents) and environmental exposure . Thermoplastic variants (e.g., PP, PVC) offer lightweight, non-conductive alternatives for chemical and electrical applications . Material selection ensures longevity exceeding 20 years in demanding conditions. -
High-Pressure and Temperature Tolerance Engineered for extreme operating conditions, male thread connectors maintain integrity under pressures up to 6,000 PSI (413 bar) and temperatures from -200°C to 400°C . Precision-machined threads and reinforced shoulders prevent deformation under cyclic stress, making them suitable for hydraulic, steam, and industrial process systems. -
Easy Installation and Reusability The simple screw-on design enables quick assembly without specialized tools, reducing labor time by up to 50% compared to welded joints . Reusable threads allow for disassembly and reconnection during maintenance, though sealant compounds (e.g., PTFE tape) are recommended to prevent leakage and galling . -
Vibration and Fatigue Resistance Thread engagement distributes mechanical loads evenly, dampening vibrations and mitigating fatigue failure in dynamic applications . This is critical in machinery, automotive, and aerospace systems where shock and movement could compromise push-fit or quick-connect alternatives.
Typical Applications of Male Thread Connector
-
Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems: Connectors with NPT or metric threads link hoses, pumps, and cylinders in industrial machinery, ensuring leak-free performance under high-pressure cycles . -
Plumbing and Water Distribution: Brass or stainless-steel variants with BSP threads are used in potable water systems, resisting corrosion and scaling while allowing easy maintenance . -
Oil and Gas Pipelines: High-pressure carbon steel connectors with API threads join segments of drilling, refining, and transmission pipelines, withstanding sour gas and extreme temperatures . -
Chemical Processing: Stainless steel or PTFE-coated connectors handle corrosive fluids in reactors, valves, and instrumentation, complying with FDA and ISO 9001 standards for purity . -
HVAC and Refrigeration: Copper or brass connectors with ACME threads connect refrigerant lines and compressors, supporting thermal cycling and vibration resistance .
Technical Specifications
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
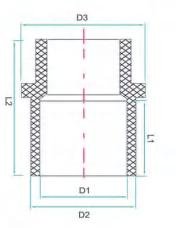
| SIZE | Number | D1 | D2 | D3 | L1 | L2 |
| DN15 | WJ15 | 20.3 | 26.3 | 28.49 | 16.5 | 34.43 |
| DN20 | WJ20 | 25.3 | 31.9 | 34.66 | 19 | 36.47 |
| DN25 | WJ25 | 32.35 | 39.95 | 41.9 | 22.5 | 45.08 |
| DN32 | WJ32 | 40.4 | 49.8 | 52 | 26.5 | 40.75 |
| DN40 | WJ40 | 50.45 | 60.25 | 62.64 | 31.5 | 56.97 |
| DN50 | WJ50 | 63.5 | 75.9 | 78.11 | 38 | 69.92 |
| DN65 | WJ65 | 75.5 | 88.91 | 91.16 | 44 | 80.54 |
| DN80 | WJ80 | 90.55 | 105.15 | 107.09 | 51.5 | 86.51 |
| DN100 | WJ100 | 110.6 | 127.39 | 129.92 | 61.5 | 109.04 |