Overview of Reducing Tee
Key Features of Reducing Tee
Optimized Flow Distribution
Robust Construction and Material Versatility
Pressure and Temperature Resilience
Installation Flexibility and Compatibility
Corrosion and Abrasion Resistance
Technical Specifications
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Typical Applications of Reducing Tee
Chemical and Process Industries
Water and Wastewater Treatment
Oil and Gas Pipeline Systems
Power Generation and HVAC Systems
Mining and Industrial Applications
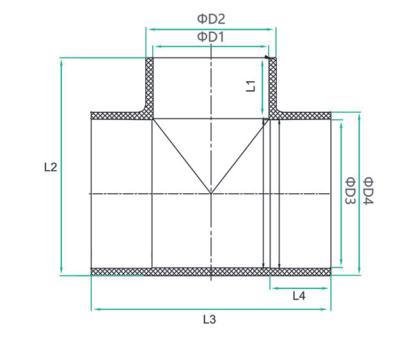
| SIZE | NO. | D1 | D2 | L1 | L2 | L3 | D3 | D4 | L4 |
| DN25x15 | Y3T25x15 | 20.3 | 26.3 | 16.5 | 53.7 | 68 | 32.25 | 39.95 | 22.5 |
| DN25x20 | Y3T25x20 | 25.3 | 31.9 | 17 | 64.3 | 81 | 40.5 | 47.5 | 26.5 |
| DN25x25 | Y3T25x25 | 25.3 | 31.9 | 17 | 74.4 | 91 | 50.45 | 57.5 | 31.5 |
| DN30x25 | Y3T30x25 | 32.5 | 38.5 | 22.5 | 58 | 98 | 50.45 | 50.25 | 31.5 |
| DN30x25 | Y3T50x25 | 32.5 | 39.95 | 22.5 | 93 | 111 | 63.5 | 75.9 | 38 |
| DN30x32 | Y3T50x32 | 40.4 | 49.8 | 26.5 | 97 | 119 | 63.5 | 75.9 | 38 |
| DN35x25 | Y3T65x25 | 32.5 | 39.95 | 22.5 | 105.6 | 123 | 75.5 | 88.91 | 44 |
| DN35x40 | Y3T65x40 | 50.45 | 60.25 | 31.5 | 115 | 141 | 75.5 | 88.91 | 44 |
| DN80x25 | Y3T80x25 | 32.5 | 39.95 | 22.5 | 120.8 | 137.9 | 90.55 | 105.15 | 51.5 |
| DN80x40 | Y3T80x40 | 50.45 | 60.25 | 31.5 | 130.5 | 156 | 90.55 | 105.15 | 51.5 |
| DN80x50 | Y3T80x50 | 63.5 | 75.9 | 38 | 137 | 169 | 90.55 | 105.15 | 31.5 |
| DN100x25 | Y3T100x25 | 32.5 | 39.95 | 22.5 | 142.6 | 158 | 110.6 | 127.39 | 61.5 |
| DN100x50 | Y3T100x50 | 63.5 | 75.9 | 38 | 156 | 189 | 110.6 | 127.39 | 61.5 |
| DN100x65 | Y3T100x65 | 75.5 | 88.91 | 34 | 164.2 | 200.96 | 110.6 | 127.39 | 61.5 |
| DN125x25 | Y3T125x25 | 32.5 | 39.95 | 22.5 | 180 | 197 | 120.6 | 140.3 | 76 |
| DN125x50 | Y3T125x50 | 90.55 | 106.15 | 51.5 | 203.8 | 246 | 140 | 161.4 | 76 |
| DN150x50 | Y3T150x50 | 63.5 | 75.9 | 38 | 211.5 | 240.5 | 140.7 | 184.5 | 86.5 |
| DN150x100 | Y3T125x100 | 110.6 | 127.39 | 61.5 | 234.3 | 287.5 | 160.7 | 184.5 | 86.5 |
| dn200x110 | Y3T200x110 | 110 | 127.5 | 61.5 | 277.5 | 356 | 201.1 | 228.1 | 106.2 |
| dn200x160 | Y3T200x160 | 160 | 184.9 | 86.5 | 302.35 | 376 | 200 | 228.1 | 106.2 |
| DN200x100 | Y3T200x100 | 110.6 | 127.39 | 61.5 | 302.3 | 352 | 226.2 | 253.8 | 118.5 |
| DN200x150 | Y3T200x150 | 160.7 | 184.5 | 86.5 | 327.2 | 401.5 | 226.2 | 253.8 | 118.5 |
| dn250x110 | Y3T250x110 | 110 | 127.5 | 61.5 | 330.5 | 429 | 250 | 283.4 | 131.5 |
| dn250x160 | Y3T250x160 | 160 | 184.9 | 86.5 | 355.2 | 429 | 250 | 283.4 | 131.5 |
| DN300x100 | Y3T300x100 | 226.2 | 253.8 | 120 | 442 | 525 | 287.5 | 315.3 | 147 |
| DN300x200 | Y3T300x200 | 226.2 | 253.8 | 120 | 440 | 564 | 317.5 | 355 | 147 |
| DN300x150 | Y3T300x150 | 160.8 | 185 | 87 | 427 | 564 | 317.5 | 355 | 165 |
| DN350x300 | Y3T350x300 | 316.7 | 355 | 165 | 546 | 696 | 356.8 | 395 | 185 |
| DN350x200 | Y3T350x200 | 226.2 | 253.8 | 120 | 501 | 696 | 356.8 | 395 | 185 |
| DN400x300 | Y3T400x300 | 316.7 | 355 | 165 | 593 | 740 | 402 | 442 | 208 |
| DN400x200 | Y3T400x200 | 226.2 | 253.8 | 120 | 548 | 740 | 402 | 442 | 208 |